Note
Click here to download the full example code
Plotting data points¶
GMT shines when it comes to plotting data on a map. We can use some sample data that is
packaged with GMT to try this out. PyGMT provides access to these datasets through the
pygmt.datasets package. If you don’t have the data files already, they are
automatically downloaded and saved to a cache directory the first time you use them
(usually ~/.gmt/cache).
import pygmt
For example, let’s load the sample dataset of tsunami generating earthquakes around
Japan (pygmt.datasets.load_japan_quakes). The data is loaded as a
pandas.DataFrame.
data = pygmt.datasets.load_japan_quakes()
# Set the region for the plot to be slightly larger than the data bounds.
region = [
data.longitude.min() - 1,
data.longitude.max() + 1,
data.latitude.min() - 1,
data.latitude.max() + 1,
]
print(region)
print(data.head())
Out:
['libgmt.so']
[131.29, 150.89, 34.02, 50.77]
year month day latitude longitude depth_km magnitude
0 1987 1 4 49.77 149.29 489 4.1
1 1987 1 9 39.90 141.68 67 6.8
2 1987 1 9 39.82 141.64 84 4.0
3 1987 1 14 42.56 142.85 102 6.5
4 1987 1 16 42.79 145.10 54 5.1
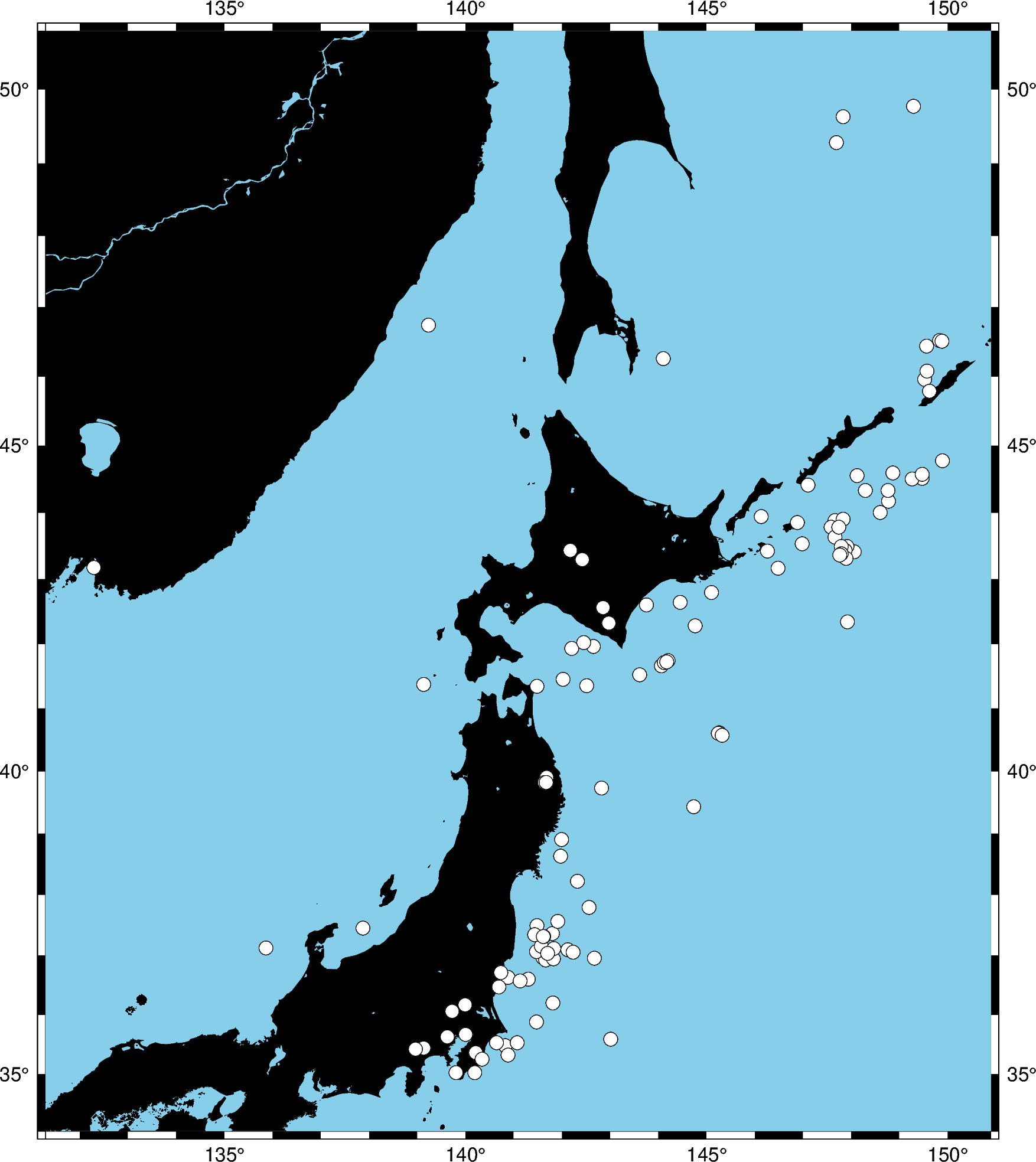
We’ll use pygmt.Figure.plot method to plot circles on the locations of the
hypocenters of the earthquakes.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.basemap(region=region, projection="M8i", frame=True)
fig.coast(land="black", water="skyblue")
fig.plot(x=data.longitude, y=data.latitude, style="c0.3c", color="white", pen="black")
fig.show()
Out:
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
We used the style c0.3c which means “circles of 0.3 centimeter size”. The pen
attribute controls the outline of the symbols and the color controls the fill.
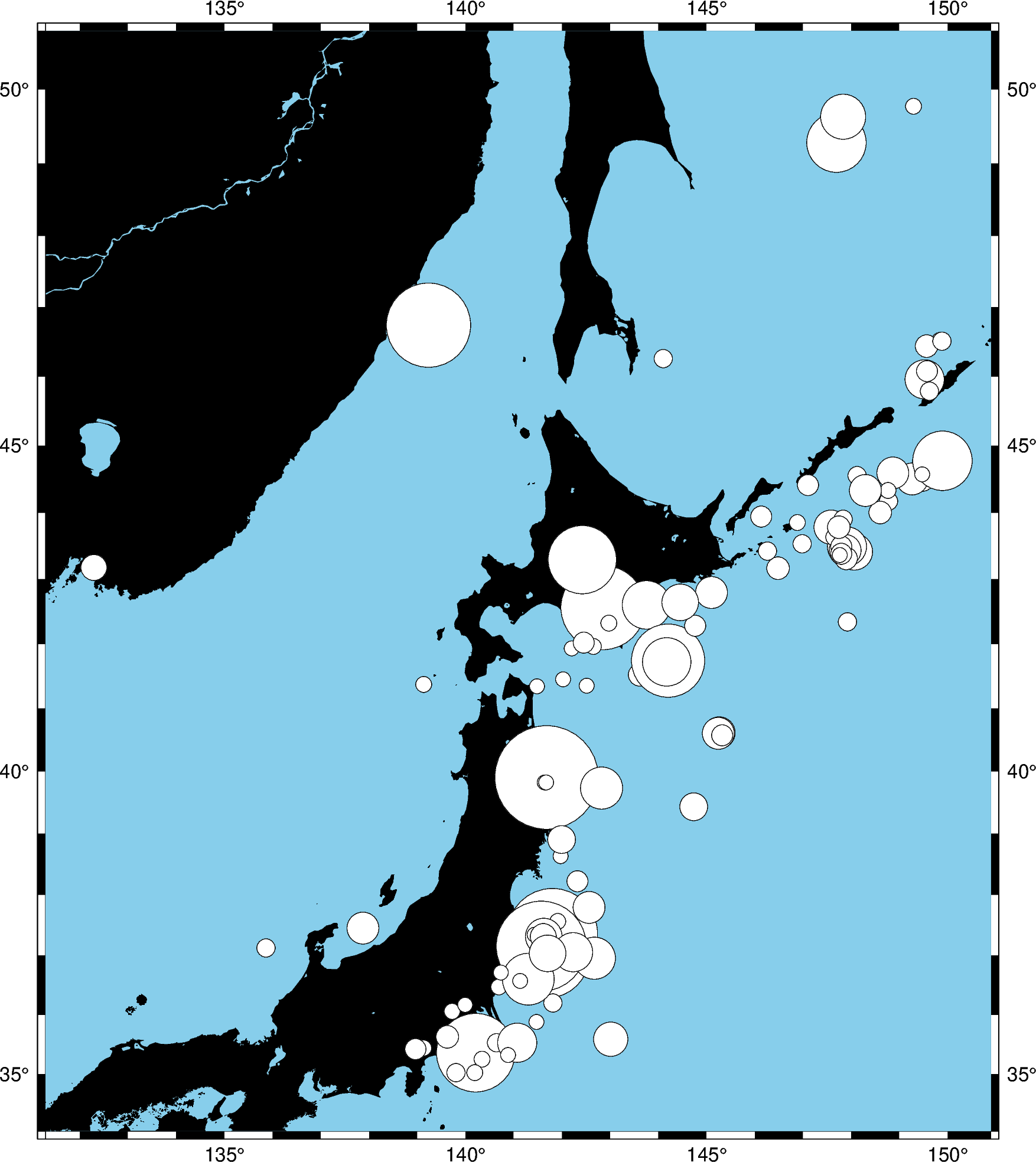
We can map the size of the circles to the earthquake magnitude by passing an array to
the sizes argument. Because the magnitude is on a logarithmic scale, it helps to
show the differences by scaling the values using a power law.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.basemap(region=region, projection="M8i", frame=True)
fig.coast(land="black", water="skyblue")
fig.plot(
x=data.longitude,
y=data.latitude,
sizes=0.02 * (2 ** data.magnitude),
style="cc",
color="white",
pen="black",
)
fig.show()
Out:
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Notice that we didn’t include the size in the style argument this time, just the
symbol c (circles) and the unit c (centimeter). So in this case, the sizes
will be interpreted as being in centimeters.
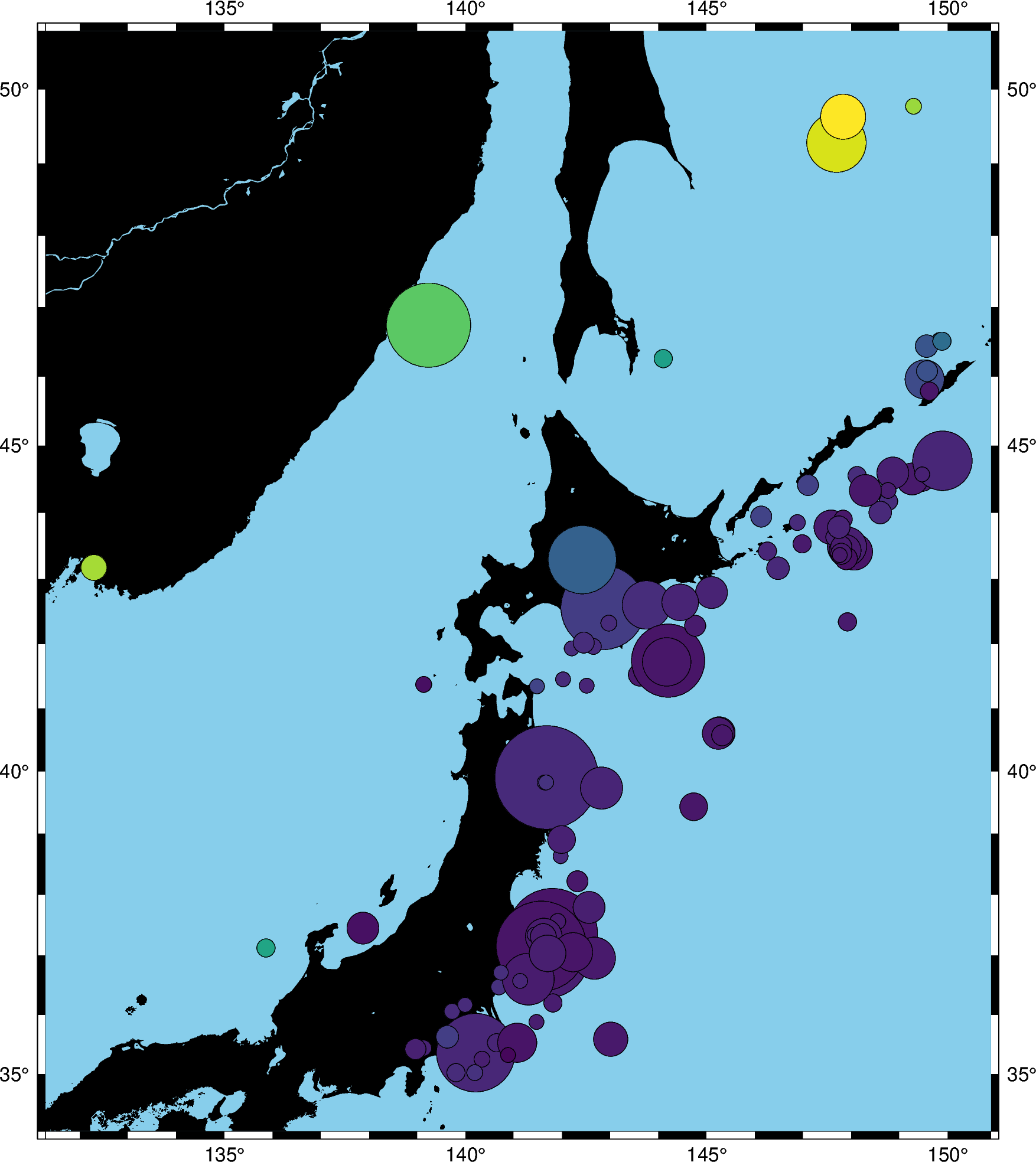
We can also map the colors of the markers to the depths by passing an array to the
color argument and providing a colormap name (cmap). We can even use the new
matplotlib colormap “viridis”.
fig = pygmt.Figure()
fig.basemap(region=region, projection="M8i", frame=True)
fig.coast(land="black", water="skyblue")
fig.plot(
x=data.longitude,
y=data.latitude,
sizes=0.02 * 2 ** data.magnitude,
color=data.depth_km / data.depth_km.max(),
cmap="viridis",
style="cc",
pen="black",
)
fig.show()
Out:
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
['libgmt.so']
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
Note
We normalize the data values given to color because, by default,
plot can only interpret values between 0 and 1. To use the
actual data values, we would need to create a color palette table (CPT) which
isn’t implemented yet.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 4.267 seconds)